This tutorial explains how to launch an Avalanche Validator node using AWS Marketplace. It includes instructions for subscribing to the software, configuring it, launching it, accessing the EC2 console, and changing the node configuration to sync the Fuji testnet. The tutorial includes the steps for setting up a Keypair for ssh access, the ssh command to access the EC2 instance, and the curl command to confirm the networkID of the synced network.
Introduction
Avalanche is a highly scalable and interoperable open-source ecosystem for launching decentralized apps and enterprise blockchain solutions. Designed for global finance, it features fast transaction finalization. Ava Labs recently introduced a way to easily launch an Avalanche Validator node through the AWS Marketplace, making it easier for developers and entrepreneurs to join the Avalanche ecosystem. This guide will outline the steps for setting up and running a node on the Avalanche Fuji testnet.
Product Overview
Get the Avalanche Validator node on AWS Marketplace with a product overview that includes description, pricing, usage instructions, support details, and customer reviews. Click “Continue to Subscribe” after review.
Subscribe to This Software
Once on the “Subscribe to this Software” page you will see a button which enables you to subscribe to this AWS Marketplace offering. In addition you’ll see Terms of service including the seller’s End User License Agreement and the AWS Privacy Notice. After reviewing these you want to click on the “Continue to Configuration” button.
Configure This Software
This page lets you choose a fulfillment option and software version to launch this software. No changes are needed as the default settings are sufficient. Leave the Fulfillment Option as 64-bit (x86) Amazon Machine Image (AMI). The software version is the latest build of the AvalancheGo full node, v1.9.5 (Dec 22, 2022), AKA Banff.5. This will always show the latest version. Also, the Region to deploy in can be left as US East (N. Virginia). On the right you’ll see the software and infrastructure pricing. Lastly, click the “Continue to Launch” button.
Launch This Software
Here you can review the launch configuration details and follow the instructions to launch the Avalanche Validator Node. The changes are very minor. Leave the action as “Launch from Website.” The EC2 Instance Type should remain c5.2xlarge. The primary change you’ll need to make is to choose a keypair which will enable you to ssh into the newly created EC2 instance to run curl commands on the Validator node. You can search for existing Keypairs or you can create a new keypair and download it to your local machine. If you create a new keypair you’ll need to move the keypair to the appropriate location, change the permissions and add it to the OpenSSH authentication agent. For example, on MacOS it would look similar to the following:
# In this example we have a keypair called avalanche.pem which was downloaded from AWS to ~/Downloads/avalanche.pem # Confirm the file exists with the following command test -f ~/Downloads/avalanche.pem && echo "avalance.pem exists." # Running the above command will output the following: # avalance.pem exists. # Move the avalanche.pem keypair from the ~/Downloads directory to the hidden ~/.ssh directory mv ~/Downloads/avalanche.pem ~/.ssh # Next add the private key identity to the OpenSSH authentication agent ssh-add ~/.ssh/avalanche.pem; # Change file modes or Access Control Lists sudo chmod 600 ~/.ssh/avalanche.pem
Once these steps are complete you are ready to launch the Validator node on EC2. To make that happen click the “Launch” button
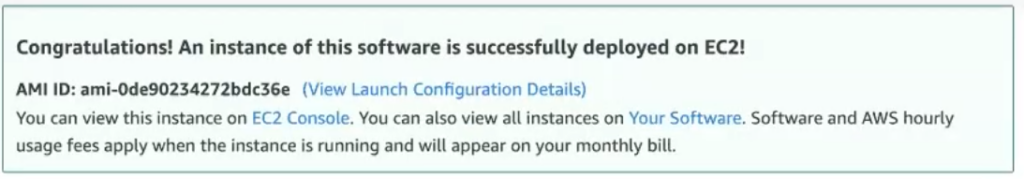
You now have an Avalanche node deployed on an AWS EC2 instance! Copy the AMI ID and click on the EC2 Console link for the next step.
EC2 Console
Now take the AMI ID from the previous step and input it into the search bar on the EC2 Console. This will bring you to the dashboard where you can find the EC2 instances public IP address.
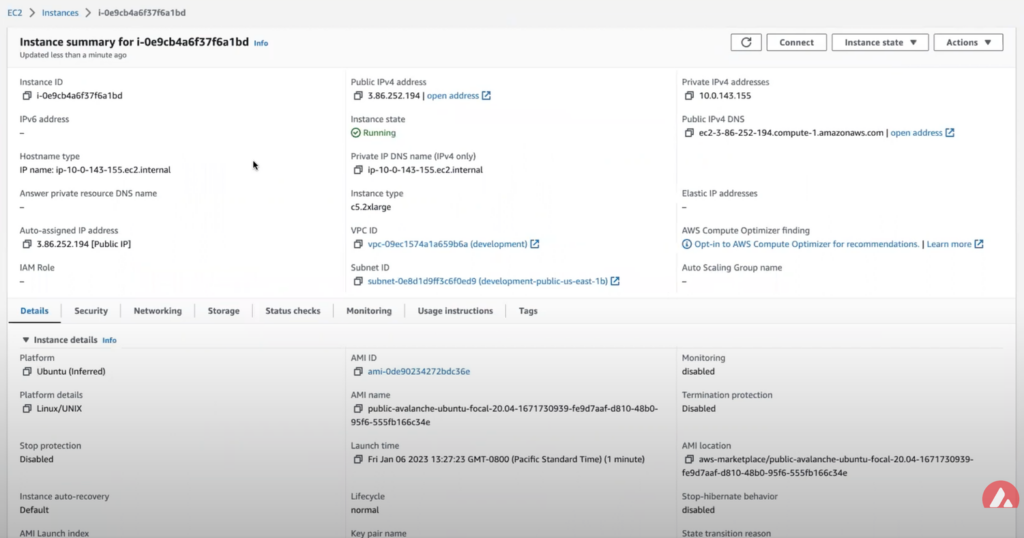
Copy that public IP address and open a Terminal or command line prompt. Once you have the new Terminal open ssh into the EC2 instance with the following command.
ssh username@ip.address.of.ec2.instance
Node Configuration
Switch to Fuji Testnet
By default the Avalanche Node available through the AWS Marketplace syncs the Mainnet. If this is what you are looking for, you can skip this step.
For this tutorial you want to sync and validate the Fuji Testnet. Now that you’re sshed into the EC2 instance you can make the required changes to sync Fuji instead of Mainnet.
First, confirm that the node is syncing the Mainnet by running the info.getNetworkID command.
info.getNetworkID Request
curl -X POST --data '{
"jsonrpc":"2.0",
"id" :1,
"method" :"info.getNetworkID",
"params": {
}
}' -H 'content-type:application/json;' 127.0.0.1:9650/ext/info
info.getNetworkID Response
The returned networkID will be 1 which is the network ID for Mainnet.
{
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"result": {
"networkID": "1"
},
"id": 1
}
Now you want to edit /etc/avalanchego/conf.json and change the "network-id" property from "mainnet" to "fuji". To see the contents of /etc/avalanchego/conf.json you can cat the file.
cat /etc/avalanchego/conf.json
{
"api-keystore-enabled": false,
"http-host": "0.0.0.0",
"log-dir": "/var/log/avalanchego",
"db-dir": "/data/avalanchego",
"api-admin-enabled": false,
"dynamic-public-ip": "opendns",
"network-id": "mainnet"
}
Edit that /etc/avalanchego/conf.json with your favorite text editor and change the value of the "network-id" property from "mainnet" to "fuji". Once that’s complete, save the file and restart the Avalanche node via sudo systemctl restart avalanchego. You can then call the info.getNetworkID endpoint to confirm the change was successful.
info.getNetworkID Request
curl -X POST --data '{
"jsonrpc":"2.0",
"id" :1,
"method" :"info.getNetworkID",
"params": {
}
}' -H 'content-type:application/json;' 127.0.0.1:9650/ext/info
info.getNetworkID Response
The returned networkID will be 5 which is the network ID for Fuji.
{
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"result": {
"networkID": "5"
},
"id": 1
}
Next you run the info.isBoostrapped command to confirm if the Avalanche Validator node has finished bootstrapping.
info.isBootstrapped Request
curl -X POST --data '{
"jsonrpc":"2.0",
"id" :1,
"method" :"info.isBootstrapped",
"params": {
"chain":"P"
}
}' -H 'content-type:application/json;' 127.0.0.1:9650/ext/info
Once the node is finished bootstrapping, the response will be:
info.isBootstrapped Response
{
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"result": {
"isBootstrapped": true
},
"id": 1
}
Note that initially the response is false because the network is still syncing.
When you’re adding your node as a Validator on the Avalanche Mainnet you’ll want to wait for this response to return true so that you don’t suffer from any downtime while validating. For this tutorial you’re not going to wait for it to finish syncing as it’s not strictly necessary.
info.getNodeID Request
Next, you want to get the nodeID which will be used to add the node as a Validator. To get the node’s ID you call the info.getNodeID jsonrpc endpoint.
curl --location --request POST 'http://127.0.0.1:9650/ext/info' \
--header 'Content-Type: application/json' \
--data-raw '{
"jsonrpc":"2.0",
"id" :1,
"method" :"info.getNodeID",
"params" :{
}
}'
info.getNodeID Response
Take a note of the nodeID value which is returned as you’ll need to use it in the next step when adding a validator via the Avalanche Web Wallet. In this case the nodeID is NodeID-Q8Gfaaio9FAqCmZVEXDq9bFvNPvDi7rt5
{
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"result": {
"nodeID": "NodeID-Q8Gfaaio9FAqCmZVEXDq9bFvNPvDi7rt5",
"nodePOP": {
"publicKey": "0x85675db18b326a9585bfd43892b25b71bf01b18587dc5fac136dc5343a9e8892cd6c49b0615ce928d53ff5dc7fd8945d",
"proofOfPossession": "0x98a56f092830161243c1f1a613ad68a7f1fb25d2462ecf85065f22eaebb4e93a60e9e29649a32252392365d8f628b2571174f520331ee0063a94473f8db6888fc3a722be330d5c51e67d0d1075549cb55376e1f21d1b48f859ef807b978f65d9"
}
},
"id": 1
}
Add Node as Validator on Fuji via the Web Wallet
For adding the new node as a Validator on the Fuji testnet’s Primary Network you can use the Avalanche Web Wallet.
The Avalanche Web Wallet is a web-based application with no middleware or any kind of server communication. It can be either accessed online or compiled and run locally. The Avalanche Web Wallet is a multi-faceted jewel and offers validation/delegation, cross-chain transfers, reward estimation, asset/key management, and more.
Switching the Connected Network
Check which network the wallet is connected to by looking at the top right of the screen. By default the Avalanche Web Wallet connects to Mainnet.
Connected to Mainnet
For the sake of this demo you want to connect the Wallet to the Fuji Testnet. At the top right of the wallet click “Mainnet” and from the nav menu select Fuji.
Selecting Fuji
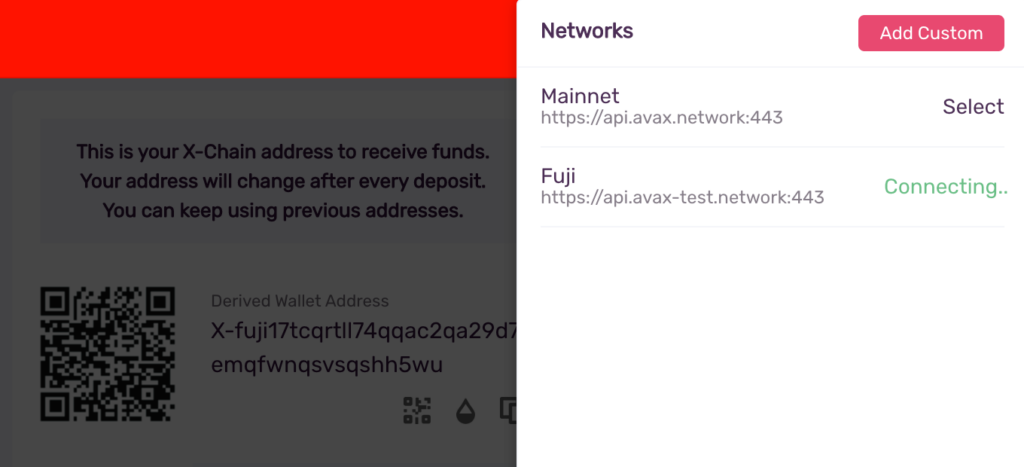
The wallet will display “Connecting…” while it is switching from Mainnet to Fuji.
Connected to Fuji
Once the wallet has connected to Fuji a popup will display “Connected to Fuji”
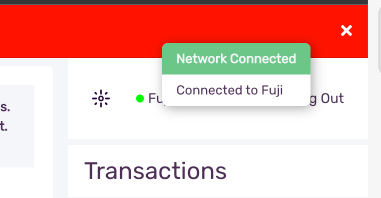
Connected to Fuji
You can follow the same steps for switching back to Mainnet from Fuji and for adding custom networks.
The Earn Tab
To add a node as a Validator, first select the “Earn” tab in the left hand nav menu. Next click the “Add Validator” button.
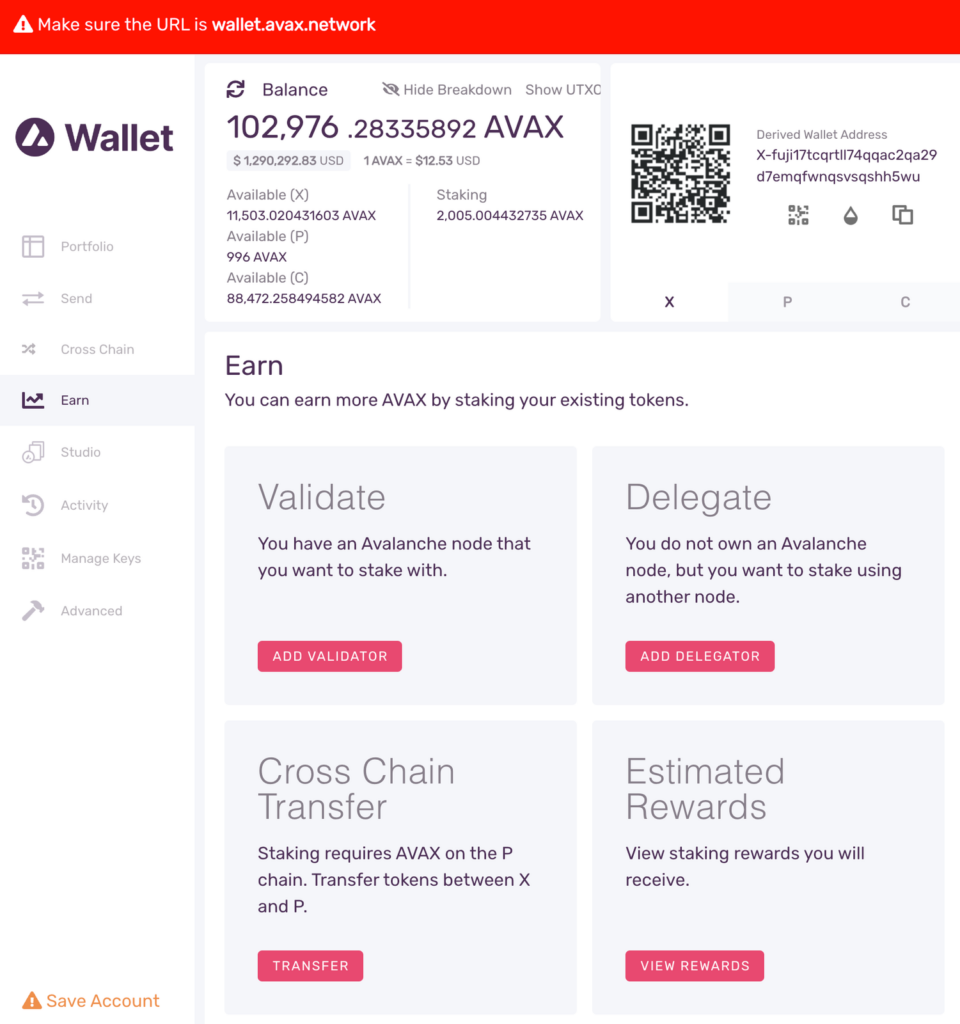
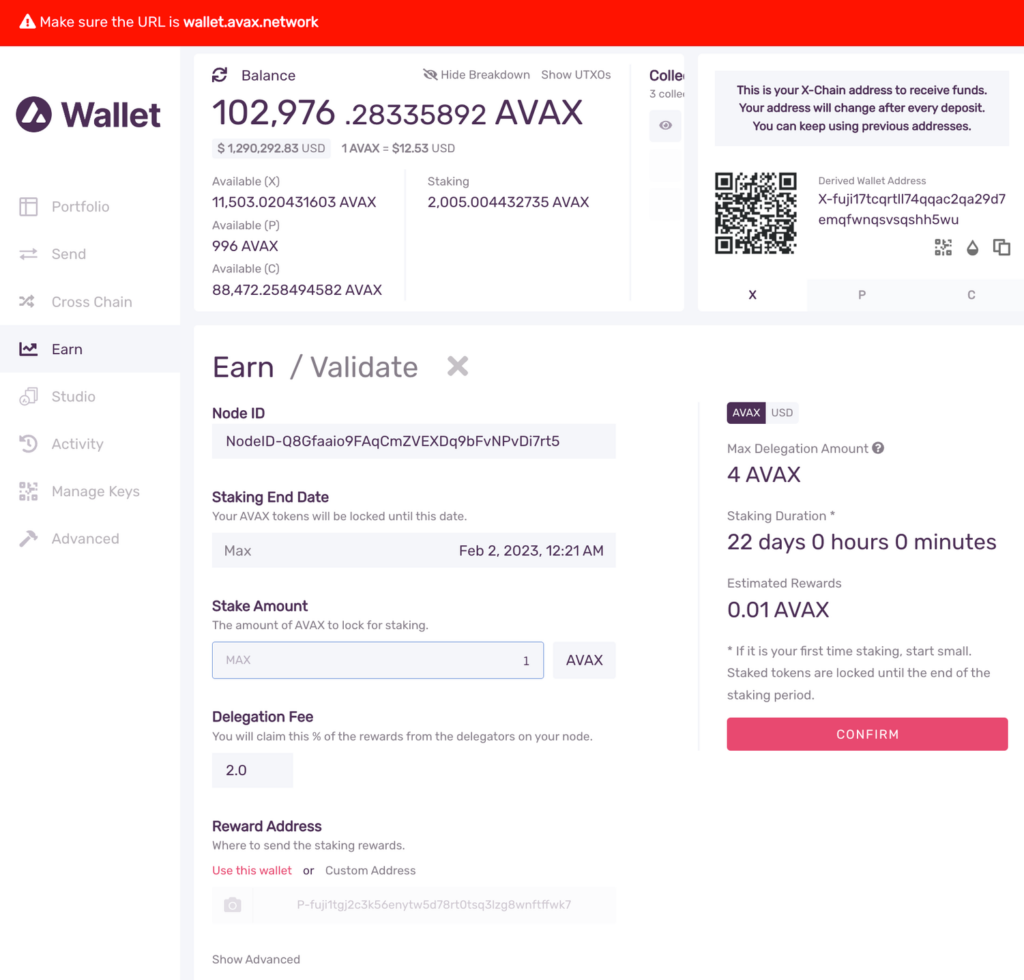
The Earn / Validate Form
Let’s look at the input values for the Earn / Validate form.
-
Node ID: A unique ID derived from each individual node’s staker certificate. Use the
NodeIDwhich was returned in theinfo.getNodeIDresponse. In this example it’sNodeID-Q8Gfaaio9FAqCmZVEXDq9bFvNPvDi7rt5 -
Staking End Date: Your AVAX tokens will be locked until this date.
-
Stake Amount: The amount of AVAX to lock for staking. On Mainnet the minimum required amount is 2,000 AVAX. On Testnet the minimum required amount is 1 AVAAX.
-
Delegation Fee: You will claim this % of the rewards from the delegators on your node.
-
Reward Address: A reward address is the destination address of the accumulated staking rewards.
Fill the fields and confirm! Carefully check the details, and click “Submit”!
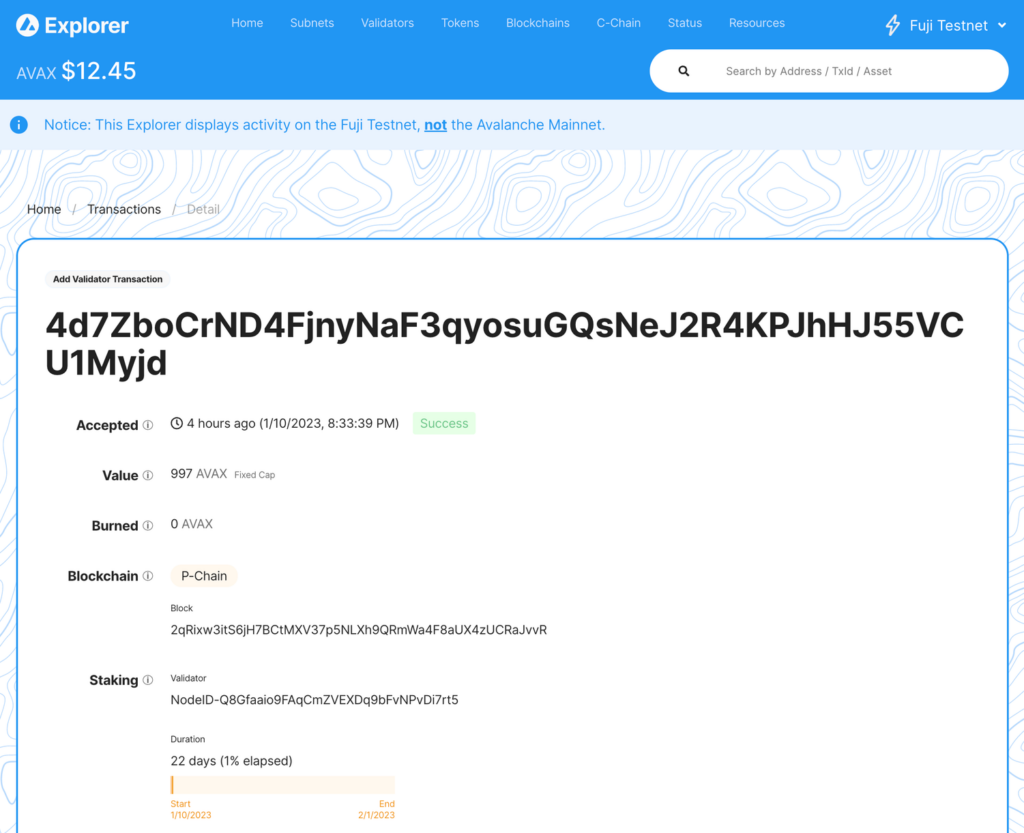
The AddValidatorTx Transaction
Once the transaction is successfully issued to the Avalanche Network the list of transactions in the right column will update with the new AddValidatorTx pushed to the top of the list. Click the magnifying glass icon and a new browser tab will open with the details of the AddValidatorTx. It will show details such as the total value of AVAX transferred, any AVAX which were burned, the blockchainID, the blockID, the nodeID of the validator, and the total time which has elapsed from the entire Validation period.
Confirm That the Node is a Pending Validator on Fuji
As a last step you can call the platform.getPendingvalidators endpoint to confirm that the Avalanche node which was recently spun up on AWS is no in the pending validators queue where it will stay for 5 minutes.
platform.getPendingValidators Request
curl --location --request POST 'https://api.avax-test.network/ext/bc/P' \
--header 'Content-Type: application/json' \
--data-raw '{
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"method": "platform.getPendingValidators",
"params": {
"subnetID": "11111111111111111111111111111111LpoYY",
"nodeIDs": []
},
"id": 1
}'
platform.getPendingValidators Response
{
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"result": {
"validators": [
{
"txID": "4d7ZboCrND4FjnyNaF3qyosuGQsNeJ2R4KPJhHJ55VCU1Myjd",
"startTime": "1673411918",
"endTime": "1675313170",
"stakeAmount": "1000000000",
"nodeID": "NodeID-Q8Gfaaio9FAqCmZVEXDq9bFvNPvDi7rt5",
"delegationFee": "2.0000",
"connected": false,
"delegators": null
}
],
"delegators": []
},
"id": 1
}
You can also pass in the NodeID as a string to the nodeIDs array in the request body.
curl --location --request POST 'https://api.avax-test.network/ext/bc/P' \
--header 'Content-Type: application/json' \
--data-raw '{
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"method": "platform.getPendingValidators",
"params": {
"subnetID": "11111111111111111111111111111111LpoYY",
"nodeIDs": ["NodeID-Q8Gfaaio9FAqCmZVEXDq9bFvNPvDi7rt5"]
},
"id": 1
}'
This will filter the response by the nodeIDs array which will save you time by no longer requiring you to search through the entire response body for the NodeIDs.
{
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"result": {
"validators": [
{
"txID": "4d7ZboCrND4FjnyNaF3qyosuGQsNeJ2R4KPJhHJ55VCU1Myjd",
"startTime": "1673411918",
"endTime": "1675313170",
"stakeAmount": "1000000000",
"nodeID": "NodeID-Q8Gfaaio9FAqCmZVEXDq9bFvNPvDi7rt5",
"delegationFee": "2.0000",
"connected": false,
"delegators": null
}
],
"delegators": []
},
"id": 1
}
After 5 minutes the node will officially start validating the Avalanche Fuji testnet and you will no longer see it in the response body for the platform.getPendingValidators endpoint. Now you will access it via the platform.getCurrentValidators endpoint.
platform.getCurrentValidators Request
curl --location --request POST 'https://api.avax-test.network/ext/bc/P' \
--header 'Content-Type: application/json' \
--data-raw '{
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"method": "platform.getCurrentValidators",
"params": {
"subnetID": "11111111111111111111111111111111LpoYY",
"nodeIDs": ["NodeID-Q8Gfaaio9FAqCmZVEXDq9bFvNPvDi7rt5"]
},
"id": 1
}'
platform.getCurrentValidators Response
{
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"result": {
"validators": [
{
"txID": "2hy57Z7KiZ8L3w2KonJJE1fs5j4JDzVHLjEALAHaXPr6VMeDhk",
"startTime": "1673411918",
"endTime": "1675313170",
"stakeAmount": "1000000000",
"nodeID": "NodeID-Q8Gfaaio9FAqCmZVEXDq9bFvNPvDi7rt5",
"rewardOwner": {
"locktime": "0",
"threshold": "1",
"addresses": [
"P-fuji1tgj2c3k56enytw5d78rt0tsq3lzg8wnftffwk7"
]
},
"validationRewardOwner": {
"locktime": "0",
"threshold": "1",
"addresses": [
"P-fuji1tgj2c3k56enytw5d78rt0tsq3lzg8wnftffwk7"
]
},
"delegationRewardOwner": {
"locktime": "0",
"threshold": "1",
"addresses": [
"P-fuji1tgj2c3k56enytw5d78rt0tsq3lzg8wnftffwk7"
]
},
"potentialReward": "5400963",
"delegationFee": "2.0000",
"uptime": "0.0000",
"connected": false,
"delegators": null
}
]
},
"id": 1
}
Mainnet
All of these steps can be applied to Mainnet. However, the minimum required Avax token amounts to become a validator is 2000 on the Mainnet. For more information, please read this doc.
Summary
Avalanche is the first decentralized smart contracts platform built for the scale of global finance, with near-instant transaction finality. Now with an Avalanche Validator node available as a one-click install from the AWS Marketplace developers and entrepreneurs can on-ramp into the Avalanche ecosystem in a matter of minutes. If you have any questions or want to follow up in any way please join our Discord server at https://chat.avax.network. For more developer resources please check out our Developer Documentation.

